Introduction
Engineering, Procurement, Construction, Installation and Commissioning (EPCIC) is the most commonly used form of project life cycle in the oil and gas industry. These projects are usually complex and large scale; with multiple client, main contractor, sub-contractors, vendors, consultants interfaces. In addition, the project phases are often happening at different timing, geographic locations, and with complex overlapping and milestones dependency. In addition, these projects are usually fast tracked and on a very tight schedule.
Typically during an EPCIC project, starting from engineering design stage, multitude of safety studies and risk assessments are conducted, e.g. HAZOP, HAZID, Construction Risk Assessment (CRA), Safety Integrity Level (SIL), the Formal Safety Assessments (FSAs). The general objectives of these studies and assessments are to identify any potential safety issues and then provide recommendations to close the gap or resolve the issues. It is common that for each stage of the project, easily 100s to 1000s of actions/ recommendations generated, which needs to be tacked, signed off and reported on a very tight schedule.
The Problem
One of the common issue faced during an EPCIC project is the lack of an effective actions tracking management system that caters for the complexity of the projects. The process is often underestimated and traditionally done in a less organized manner, e.g. via emails, hard paper copies and excel sheets revisions.
The most typical action tracking management process requires an action sheet to be printed out, passed around for responses and then gets approved by the corresponding “approval routes”. The process becomes more complicated when the approvers are from different organizations or different geographical locations, it is painful when the paper action close out sheets get held up by certain discipline and just are tedious to trace.
The approach is prone to mismanagement, e.g. losing track of actions; losing track of high priority items; fragmented excel sheets capturing various discipline responses; lack of alerts to parties holding up the approvals; and lack of overall visibility of the status.
The Example
The consequence of mismanagement of these actions are often very severe and costly to mitigate. In terms of general project risk management, the following figure provide good illustration on the effectiveness of fixing an issue at different stage the project life cycle.
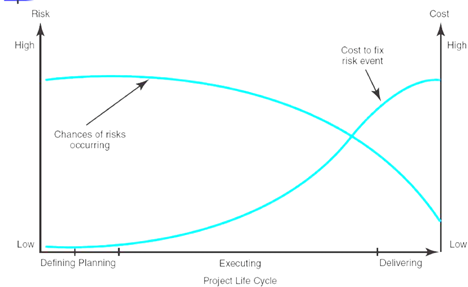
Taking a typical action from HAZOP for example; it was identified that a section of the piping is under-rated in terms of pressure tolerance, and there is risk of pipe rupture leading to flammable gas release and could result in fire and explosion.
Using the EPCIC project lifecycle as example, the original action was a simple upgrade of the pipe thickness and rating during the Engineering stage, which require very little effort (update on the engineering drawing) and almost no financial implication on the overall project cost.
If this wasn’t tracked and closed in a timely manner, and the project has moved into Procurement phase and procured a wrongly specified pipe, then the cost of additional material, and the schedule impact due to the delivery of new piping would be more significant and costly to manage.
As the project lifecycle advances, the effort and cost to fix the problem get exponentially high. For the same example, if the pipe specification is not replaced, then at a stage, the design would become too complex to change, and additional pressure relieve valves and vent stack is now required to mitigate the issue. If this happens during Installation phase at offshore location (which is usually in the middle of no where), then a lot of additional resources would be required. In the worst case scenario where the action is totally missed out and not acted on, the pipe could have eventually burst and result in an explosion event which could have taken multiple lives.
The Solution – Your Engineered Workflow Solution
With this in mind, we have developed an Engineered Workflow Solution (part of eHS Tools application suite). The eHS Tools is designed by engineer who fully understand the existing traditional action tracking management process, the pain and issues; and aimed to address the various weakness.
It is designed for qualitative and quantitative risk assessments such as HAZOP, HAZID, Construction Risk Assessments (CRA), Risk Register, QRA, Ship Collisions Study, etc.; and can even be used to track any other project actions as well.
The tool is a digital workflow solution designed to automate the action tracking process and improve productivity while embarking on a digital transformation journey.

The Technology
The eHS Tools is cloud based, hosted on Amazon Web Services, with secure https login using the company email id. The framework is based on Django, Python, REACT and various data-science technologies, which enables quick access to the databases and fast rendering of the webpage. What this meant for you:
- Browser based application (Software as a Services- SaaS). Accessible via PC, mobile phones, tablets etc. and does not require powerful machine.
- Secured HTTPs site login, for unlimited users and not organizations specific; no more VPN or firewall issue.
- Secure and independent database, i.e. all authorised users have access to the attachments, evidences and data; without all shared folder accessibility issue. In addition of frequent back up of the database.
The User Experience
What set us apart from the other available tools in the market is that the eHS Tools is designed with user friendliness in mind. It is designed to suit your existing workflow such that user can just login and intuitively use the software effectiveness. The main objective is to embark on the digital transformation journey:
- Improving the productivity.
- Intuitive user interface
- Few clicks away from any actions submission and approval
- Automated workflow, seamless distribution of actions and approval routes
- Integration with your management system, e.g. risk matrix
- Precise and clean dashboard showing critical information for planning and decision making
- Effective and live status tracking
- Live reporting page and charts providing real-time monitoring of the status, with capability to be expanded and drilled down to exact details;
- Automated email reminder and tracking of the due dates, follow up actions etc.
- Automated report and close out sheets generations with downloadable dabase and attachments
- Security and Audit Proof
- Daily backup
- Changes and trails are tracked, designed for auditing purpose.
Screen Captures
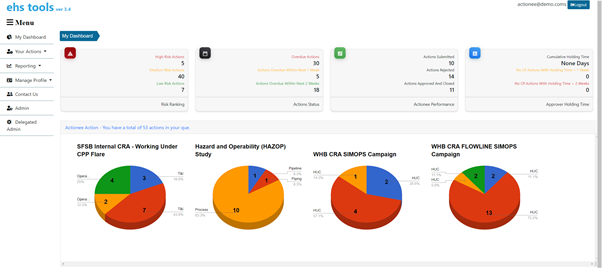
Main dashboard – clear and precise information and status
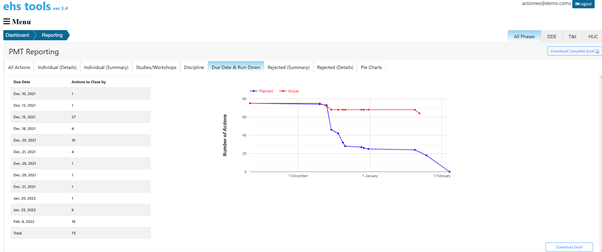
PMT Reporting – Data sorted by different project phases and provision of real-time monitoring

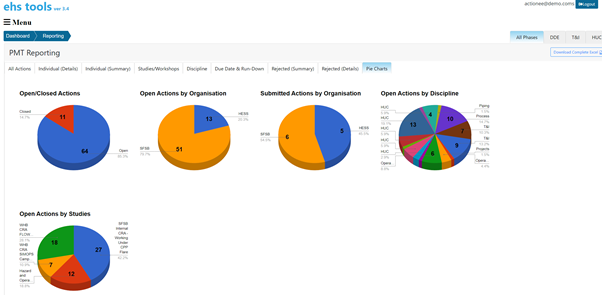
The eHS Tools is an all-in-one workflow risk management tool to streamline and promote the collaboration across the board which is designed with the user in mind. Adopt the software now and start your digital transformation today. For more information and demo request, kindly contact us.
